We can design UG-style square/round cover and CPR-style flanges specifically for each customer requirement.
As one of the most professional flexible waveguide manufacturers, Dolph Microwave manufactures a quality line of flexible twistable/non-twistable waveguides, specially designed to meet all of your requirements. The components is made from a helically wound waveguide core and additional mechanical support is offered from a variety of protective jackets.
Flexible Waveguide Definition
The Flexible Waveguide is parts of Feeder line, compared with the rigid waveguide, which is not only reduces the difficulty of connection, but also keep connection accuracy. The Rectangular Flexible Waveguide has E bend and H bend function including twisted function.
Flexible Twistable Waveguide Ordering Information
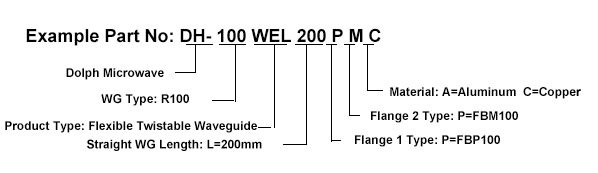
Flexible Non-twistable Waveguide Ordering Information
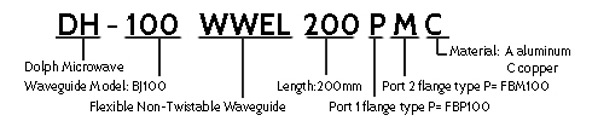
Flange type: Multiple types available - see Dolph Microwave Flanges page.
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS | |||||||||||||||||||
Waveguide Designation | Freq.Range (GHz) | Insertion Loss(dB/m) | Suggested Power Limit | Return Loss (dB) | |||||||||||||||
Peak(MW) | Average(KW) | 300mm | 600mm | 900mm | 1000mm | 1200mm | 1500mm | 1800mm | |||||||||||
R40 | WR229 flexible waveguide | WG11A | 3.22-4.90 | 0.15 | 1.6 | 5 | 31.0 | 28.8 | 28.3 | 28.3 | 27.8 | 27.3 | 26.3 | ||||||
R48 | WR187 flexible waveguide | WG12 | 3.94-5.99 | 0.16 | 1.4 | 3 | 31 | 28.8 | 28.3 | 28.3 | 26.4 | 23.1 | 21.7 | ||||||
R58 | WR159 flexible waveguide | WG13 | 4.64-7.05 | 0.18 | 0.6 | 2.5 | 31 | 28.3 | 27.8 | 27.8 | 26.4 | 23.1 | 21.7 | ||||||
R70 | WR137 flexible waveguide | WG14 | 5.38-8.17 | 0.25 | 0.56 | 2 | 30.2 | 27.8 | 27.3 | 27.3 | 26.4 | 23.1 | 21.7 | ||||||
R84 | WR112 flexible waveguide | WG15 | 6.57-9.99 | 0.3 | 0.33 | 1.5 | 30.2 | 27.3 | 27.1 | 27.1 | 26.4 | 23.1 | 21.7 | ||||||
R100 | WR90 flexible waveguide | WG16 | 8.20-12.5 | 0.4 | 0.22 | 1 | 30.2 | 27.1 | 27 | 27 | 25.2 | 22.1 | 19.7 | ||||||
R120 | WR75 flexible waveguide | WG17 | 9.84-15 | 0.5 | 0.18 | 0.75 | 29.4 | 27 | 26.4 | 26.4 | 24 | 20.93 | 19.7 | ||||||
R140 | WR62 flexible waveguide | WG18 | 11.9-18 | 0.65 | 0.12 | 0.4 | 29.4 | 26.4 | 26 | 26 | 24 | 20.93 | 19.7 | ||||||
R220 | WR42 flexible waveguide | WG20 | 17.7-26.5 | 1.2 | 0.045 | 0.1 | 23 | 22.1 | 21.1 | 21.1 | - | - | - | ||||||
R320 | WR28 flexible waveguide | WG22 | 26.5-40 | 2 | 0.022 | 0.075 | 21 | 20.8 | 20.8 | 20.8 | - | - | - | ||||||
R400 | WR22 flexible waveguide | WG23 | 33-50 | 2.5 | - | - | 20 | 16.5 | 15.6 | 16 | - | - | - | ||||||
MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS | |||||||||||||||||||
Waveguide Designation | Max Twist(Deg/m) | Min E-Bending Radii(mm) | Min H-Bending Radii(mm) | ||||||||||||||||
Static | Repeated | Static | Repeated | Static | Repeated | ||||||||||||||
R40 | WR229 flexible waveguide | WG11A | 132 | 33 | 165 | 660 | 330 | 1320 | |||||||||||
R48 | WR187 flexible waveguide | WG12 | 155 | 40 | 136 | 544 | 272 | 1088 | |||||||||||
R58 | WR159 flexible waveguide | WG13 | 185 | 45 | 116 | 464 | 232 | 928 | |||||||||||
R70 | WR137 flexible waveguide | WG14 | 210 | 52 | 100 | 400 | 200 | 800 | |||||||||||
R84 | WR112 flexible waveguide | WG15 | 260 | 68 | 82 | 328 | 164 | 656 | |||||||||||
R100 | WR90 flexible waveguide | WG16 | 315 | 76 | 66 | 264 | 132 | 528 | |||||||||||
R120 | WR75 flexible waveguide | WG17 | 365 | 92 | 54 | 216 | 108 | 432 | |||||||||||
R140 | WR62 flexible waveguide | WG18 | 445 | 112 | 46 | 184 | 92 | 368 | |||||||||||
R220 | WR42 flexible waveguide | WG20 | 630 | 157 | 30 | 120 | 60 | 240 | |||||||||||
R320 | WR28 flexible waveguide | WG22 | 920 | 230 | 20 | 80 | 40 | 160 | |||||||||||
R400 | WR22 flexible waveguide | WG23 | 920 | 230 | 18 | 78 | 38 | 158 | |||||||||||
*The Standard Model Numbers above are the most common parts ordered for size, material and flange. However, these models can easily be altered to accommodate your needs by using the Model # code system below for complete part number.
** Please refer to the Technical Reference section for flange types/connectors details. Please contact us for your specific requirements.
Dolph Flexible Waveguide refers to a crucial component in microwave engineering, specifically designed to connect rigid waveguide systems when precise positioning is challenging. Unlike rigid waveguides, which are employed in equipment rooms and for final assembly points, flexible waveguides offer adaptability in scenarios where exact alignment is unattainable.
These waveguides are constructed as thin-walled structures with folds, allowing them to bend along the H-plane, E-plane, and twist at 90º or 45º angles. Remarkably, they can undergo these variations simultaneously, offering a versatile solution for complex transmission needs. The primary purpose of flexible waveguides lies in their ability to guide specific frequency electromagnetic waves while accommodating bends and twists.
Beyond their flexibility, these waveguides also serve to isolate vibrations, address installation challenges arising from misalignments, and facilitate easier positioning and alignment. The incorporation of metal structures with mechanical and electrical interconnections forms hollow channels that exhibit waveguide behavior, contributing to their efficacy in various applications.
Dolph waveguide components supplier, their flexible Waveguide emerges as a vital element in microwave transmission, providing a dynamic and adaptable solution for scenarios requiring precise waveguide connections with bending and flexing capabilities.
Flexible waveguide use mechanically and electrically interlinked metallic structures to form a hollow channel that behaves as a waveguided with enhanced flexible and somewhat reduced performance. As the interlinked metallic structures, even if soldered and crimped, are not perfectly smooth conductive walls, the performance of flexible waveguides will not likely reach that of a traditionally manufactured waveguide. That being said, the flexible nature of these waveguide allows them to be used in applications for which rigid waveguide structures may be too bulky, unfit for the complexity of the geometries, too heavy, take too long to design/assemble, or may be unavailable during emergency repairs or retrofitting operations.
Flexible Waveguide Type: Twistable or non-twistable.
FlexibleWaveguide Size: WR137, WR112, WR90, WR75 or others.
Insertion Loss and VSWR: unit in dB.
Flexible Waveguide Length: 300, 500, 900, 1200, 1800 or other length in mm.
Flange type: Flat or groove or chock.
Hardware kits: Required or self preparation.
Any special requirement, please offer the drawing or dimension for checking.
Dolph Microwave also offer seamless waveguide with double rigid flexible design.
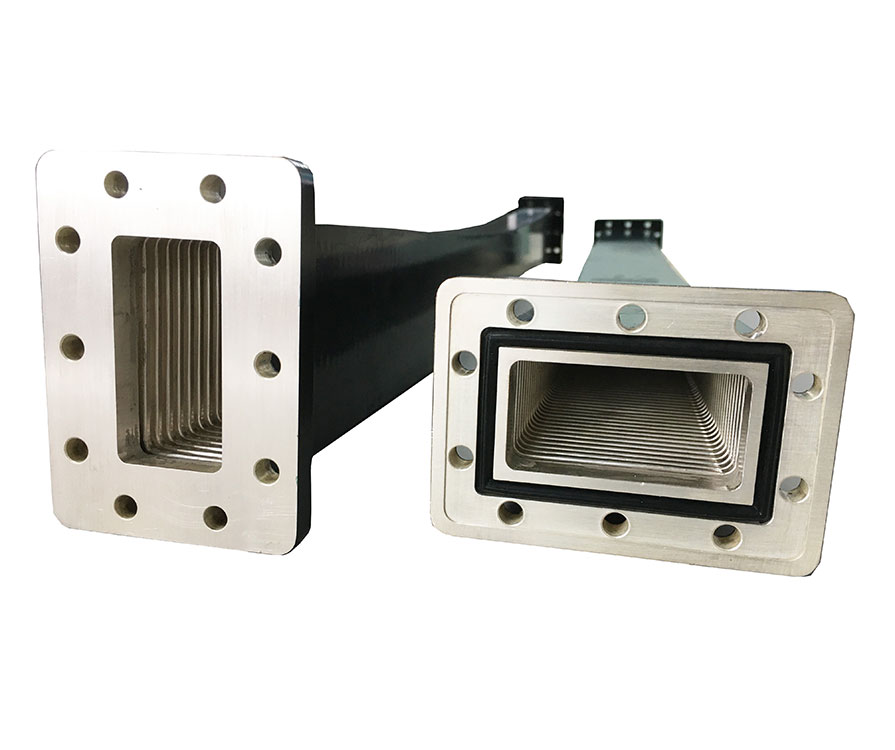
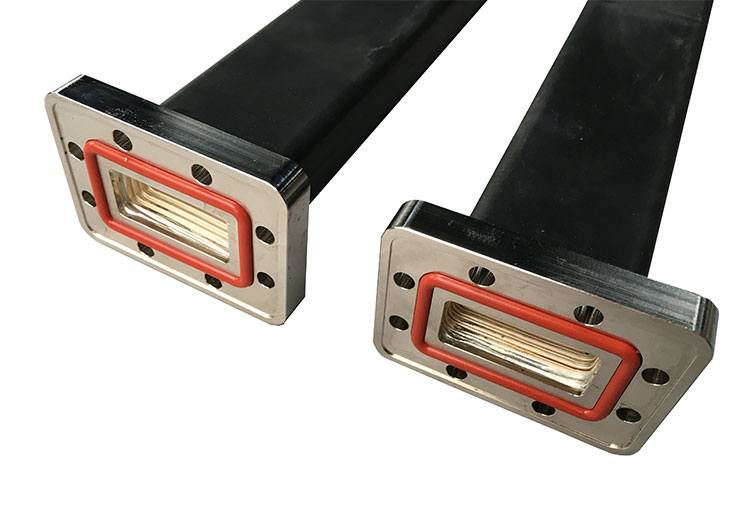


Flexible waveguide normally is for connecting different kinds of two components. Flexible waveguide is often together used with rigid waveguide systems especially if it cannot be located or positioned well. Flexible waveguide advantages offered is well outweigh the electrical performance limitations which is easy for flange and waveguide port change position. In other words is allow for mechanical movement.
Flexible waveguide are used in virtually every application that rigid waveguide are used, with the exception of extremely high power, low loss, or certain mechanical stresses are common. Waveguide systems that may require a range of adjustments, such as with satellite positioning systems, are likely to employ flexible waveguide. The bendable, and sometimes even bend/twist, nature of flex waveguide can reduce installation difficulties from misalignments common in system installation, repair, retrofitting. Flexible waveguides can also be used to isolate different sections of waveguide and mechanical structures from vibration and shock, which a rigid waveguide interconnect would not be able to do. Lastly, a flexible waveguide could be used in structures that are likely to shift or produce relative movement during thermal cycles, movement, or intense weather.
Benefits
For use in High Power Applications
Finished with high temperature paint
VSWR as low
Insertion loss
Flexible and durable neoprene sleeve
Flexible waveguide for satellite applications and other airborne and space systems include seamless flexible waveguide, flexible twistable waveguide, flexible waveguide, and semi flexible waveguide.
Flexible and twistable rectangular waveguides are used in a wide variety of Satcom, VSAT and telecom applications that carry high frequency radio.
Flexible waveguide is often used to connect two elements using rigid waveguide systems together, especially when they cannot be accurately located or positioned.. For example, flexible waveguide is often used to connect antenna systems, especially when they may not be fixed, to the base transmitter receiver system.
Other Standard Waveguide Components You may have interests in
different types of waveguide attenuators
magic tee in microwave engineering
Flexible waveguide is available in a variety of different forms. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages:
Flexible and Twistable
Flexible twistable is sealed electrically via a friction joint. This construction has the best twistable performance of all flexguides.
Flexible Waveguide
Flexible Waveguide core is wound with a solder fillet in the Interlock, thus eliminating any RF and Pressure Leakage. Flexible Waveguide will flex in the E and H planes, although pre-set twists can be incorporated during manufacture.
Flexible Seamless
Flexible/seamless offers a solution to problems where pressurization is required. It has no solder joints and therefore can easily hold pressure.
Made from helically wound silver plated brass strip
The flexible waveguide may be made from flat ribbons would on a rectangular mandrel. The edges are then convoluted or folded in and interlocked. The convoluted flexible waveguide may be left unsoldered or it may be soldered - the flexibility of the waveguide results from the flexing of each arm and not the relative sliding of the ribbons. However if it is soldered it does loose some flexibility and it is not able to be twisted to any degree.
A form of corrugated flexible waveguide may be constructed. It is manufactured by shaping thin wall rectangular tubing. It may also be made by bending and soldering corrugated sheet metal.
It is also possible to construct a bellows-style flexible waveguide using a flexible alloy.
Another common form of flexible waveguide construction is to use a helically wound system. This form of flexible waveguide is manufactured by a process of helical winding a silver coated, brass strip to form a continuous, uniform rectangular tube.
In general, flexible waveguide is jacketed in Neoprene, Silicone, Viton, Devcon or other similar materials to provide additional protection from mechanical damage while still allowing flexibility.
We can design UG-style square/round cover and CPR-style flanges specifically for each customer requirement.
Precision machining ensures accurate and lasting performance.
Flexible waveguide can be customized as per customer requirements.
Dolph Microwave flexible waveguides are in stock and ready for immediate shipment with no minimum order quantity.