Flexible waveguide products can be divided into flexible waveguide (interlocked flexible waveguide) and non-twisting flexible waveguide (seamless flexible waveguide). Flexible flexible waveguide has the bending and twisting functions of e-plane and h-plane, while non-twisting flexible waveguide has the characteristics of low loss and good air tightness.
The double-ridged flexible waveguide assembly is mainly composed of inner conductor, flange and outer sheath. The inner conductor is ridged corrugated tube, and the attenuation performance can be greatly improved by surface silver plating. Flange chooses copper or aluminum manufacturing to meet the needs of different customers; The black silicone rubber sheath can protect the soft waveguide and ensure the suitable performance of the soft waveguide in various environments.
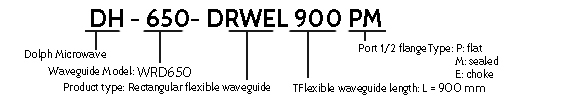
Flange type: Multiple types available - see Dolph Microwave Flanges page.
Finish: Corrosion protection plus black top coat.
For custom ridged waveguide with high quality and wide application, contact Dolph Microwave.
Product model | Frequency (GHz) | VSWR | Loss (dB/m) | Min. bending radius | Flange | |
E -(mm) | H -(mm) | |||||
DH-580DRWEL...PM | 5.8-16 | ≤1.25 | 1.5 | 105 | 210 | FP/FM |
DH-650DRWEL...PM | 6.5-18 | ≤1.30 | 1.65 | 90 | 180 | FP/FM |
DH-750DRWEL...PM | 7.5-18 | ≤1.30 | 1.65 | 85 | 170 | FP/FM |
DH-1800DRWEL...PM | 18-40 | ≤1.50 | 3.42 | 55 | 110 | FP/FM |
Wider bandwidth than rectangular waveguides.
Lower cutoff frequency compared to similar sized non-ridge waveguide.
Replacement for planar transmission lines where enhanced power handling is needed in a compact space.
Dolph Microwave also offer flexible waveguide with standard flexible designs.
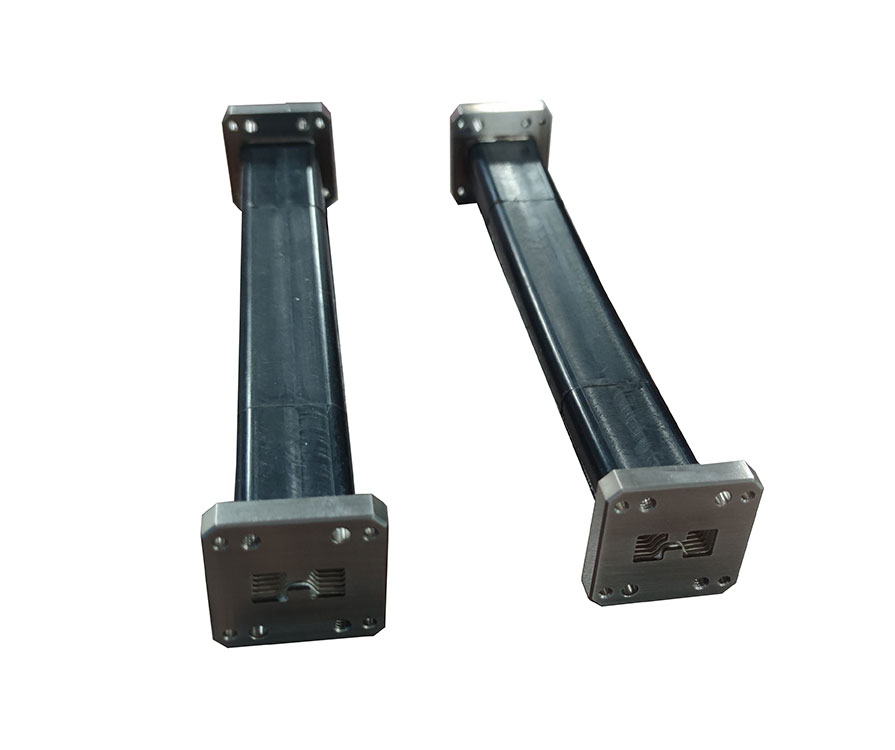
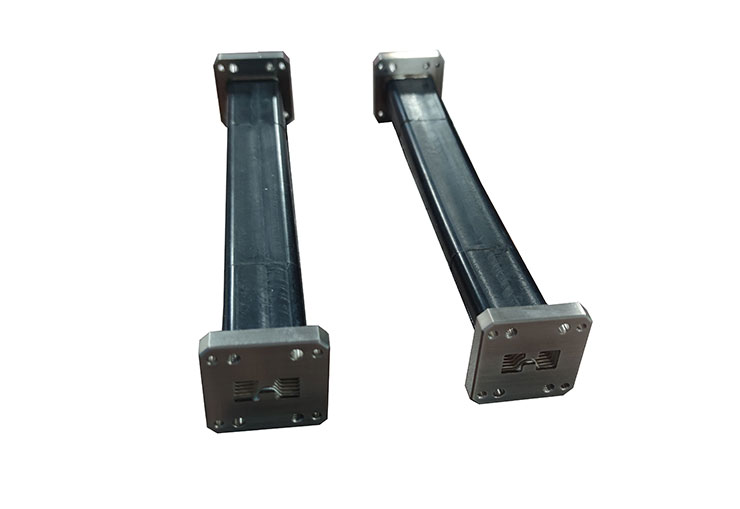


The double ridge flexible waveguide is used in situations where increased bandwidth is desired. The flexible waveguide allows mechanical movement (expansion and contraction) and also handles any vibration effects. It is often used to connect the antenna with the transmitter part of the wireless system when their positions are not fixed as well as the connection of the waveguide feeder, which can not only reduce the difficulty of connection of hard waveguide components, but ensure the connection accuracy, but also keep the electrical performance unchanged in the state of bending and torsion.
Others you may be interested in: